Long before the written word, our ancestors embarked on the earliest forms of ancient cave art.
They crafted scenes on cave walls that resonated across millennia. They provide a glimpse into the lives and beliefs of our distant ancestors.
Origins of Cave Art
Exploring the origins of cave art, it’s evident that not only Homo sapiens, but also Neanderthals contributed to these early human art forms. There are findings in Iberian Peninsula caves suggesting a rich history of cave paintings.
Pigments and markings discovered in these caves date back to over 60,000 years ago. This is 20,000 years prior to the estimated arrival of modern humans, according to archaeological assessments.
The time of homo sapiens and Neanderthals overlapped. Therefore, the debate over whether Neanderthals were the first cave painters is ongoing.
If proven, this discovery would reshape our understanding of the cognitive abilities and cultural practices of Neanderthals, emphasizing the shared capacity for symbolic expression between our two hominid lineages.
Techniques and Materials
The techniques and materials used in creating ancient cave art varied, from finger tracing to the application of natural pigments like ochre. This demonstrates the sophistication of prehistoric art techniques.
- Finger Tracing: Early artists used their fingers to draw lines and shapes directly on the cave walls, often in soft materials like clay.
- Paint Application: Pigments were applied using brushes made from animal hair, sticks, or even directly with the hands. This method allowed for a range of expressive strokes and detailed work.
- Engraving and Sculpting: Some artworks were etched into the stone with tools, creating bas-relief effects that added texture and shadow to the images.
- Blow Painting: A technique where pigment was blown onto the wall through hollow tubes, often creating a stencil effect around objects like hands.
Materials
The materials used in ancient cave paintings were sourced from the natural environment. It showcased the early artists’ deep connection with and understanding of their surroundings.
To bring their visions to life on the walls of caves, ancient artists relied on a limited yet effective palette derived from the earth itself. They used mineral pigments for color: charcoal and manganese for black, ochre for reds and yellows, and kaolin for white.
These pigments were often mixed with water, animal fat, or plant juices to create a binder. This helped the paint adhere to the cave walls and endure through millennia.
Famous Examples of Cave Art
Several examples of cave art are on display all across Europe where you can step back in time and witness firsthand early human creativity and expression.
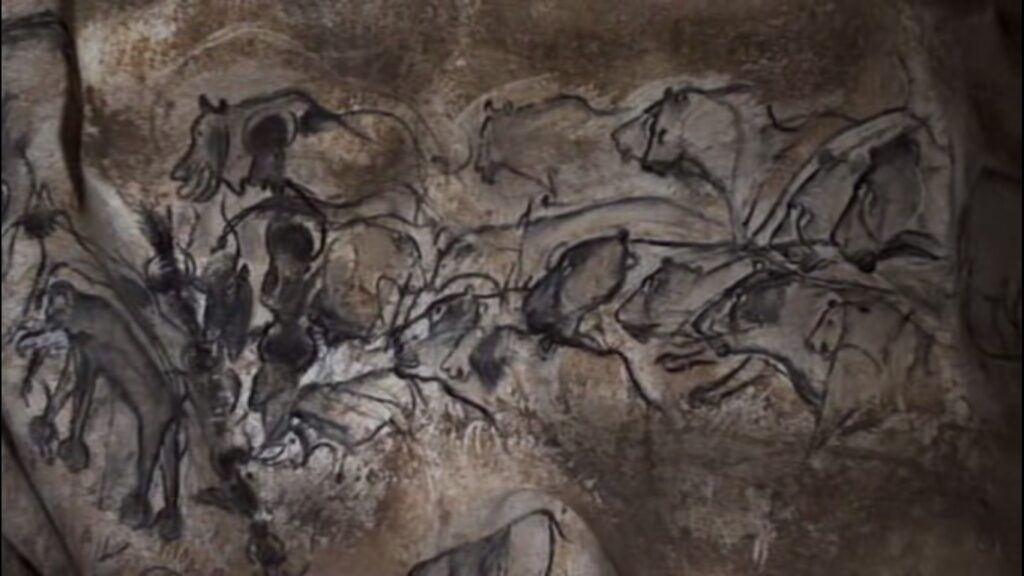
Chauvet Cave, France
Discovered in 1994, the Chauvet Cave holds some of the oldest and most detailed prehistoric art ever found. Its walls are adorned with over 400 images of animals, including horses, lions, rhinos, and bison, dating back approximately 30,000 to 32,000 years.

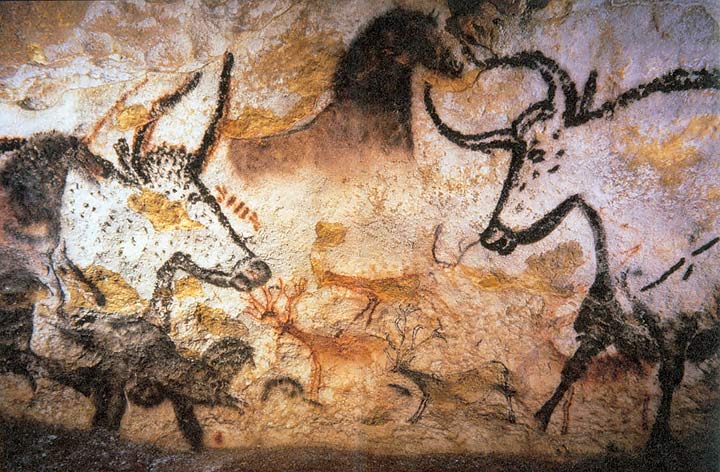
Lascaux Cave, France
Lascaux Cave, sometimes referred to as the “Sistine Chapel of Prehistory,” was discovered in 1940. It is famous for its Paleolithic cave paintings.
The most iconic section, the “Hall of Bulls,” features large paintings of bulls, horses, and deer, demonstrating a variety of techniques, including shading and color gradients. These images, dating back around 17,000 years, showcase the significance of animals in the spiritual and daily life of ancient humans.

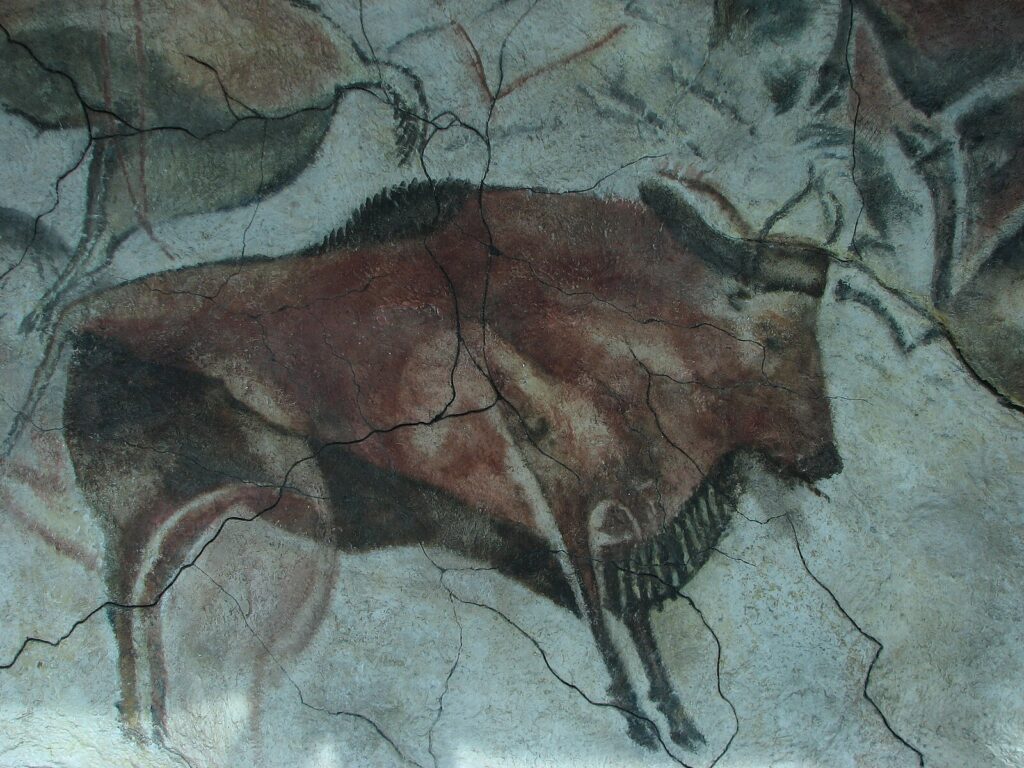
Altamira Cave, Spain
Recognized for its ceiling adorned with vibrant images of bison, the Altamira Cave paintings were created approximately 14,000 to 20,000 years ago. The discovery of Altamira, initially met with skepticism, eventually proved the existence of prehistoric art, changing the perception of ancient human societies.
The realism and depth of the paintings, achieved through the use of natural pigments and the cave’s contours, highlight the artistic and observational skills of their creators.

Cave of El Castillo, Spain
Containing the oldest known cave art in Europe, the red disk in the Cave of El Castillo has been dated to at least 40,800 years ago. It was possibly created by Neanderthals.
This cave features a variety of symbols, animals, and hand stencils. It offers insights into the development of human cognitive abilities and the potential for symbolic thought in Neanderthals.

Themes and Symbolism
The themes and symbolism in cave art, from animals to abstract signs, offer deep insights into the spiritual and cultural significance of these ancient cave paintings. Understanding these themes can provide us with insights into the minds and societies of ancient artists.
Animals
The most prevalent theme in cave art is the depiction of animals. Animals were central to the survival and spirituality of prehistoric peoples.
Animals like bison, horses, and deer are not just represented realistically. But they are often shown in dynamic scenes that may reflect hunting practices, spiritual beliefs, or the perceived qualities of these animals.
Human Figures
Though less common than animal depictions, human figures in cave art provide crucial insights into the self-perception and social structures of ancient communities. The portrayal of human figures varies from simplistic stick figures to more detailed representations, sometimes engaging in activities or rituals.
Abstract Signs
Cave art also includes a variety of abstract signs and symbols, whose meanings remain subject to interpretation. These may include dots, lines, geometric shapes, and handprints. Some researchers believe these symbols could represent calendrical information, spiritual concepts, or clan identifiers.
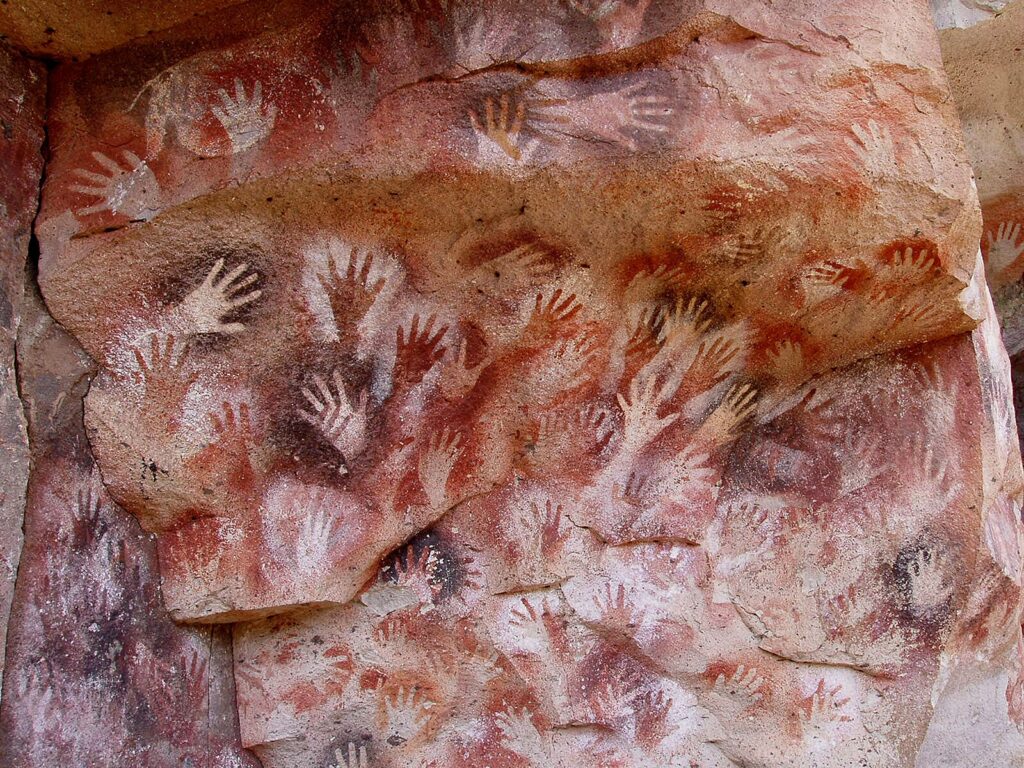
Handprints
Handprints are a form of personal signature, a direct connection between the artist and their work. They may represent ownership, identity, or a form of spiritual protection or blessing.
The Use of Space
The placement of cave paintings within the cave itself can also be significant, with some theories suggesting that certain locations were chosen for their acoustic properties or for rituals.
Conclusion
Ancient cave art provides us with invaluable insights into the lives of our ancestors. It offers us glimpses into their beliefs, rituals, and the natural world they inhabited.
Through the careful study of these paintings, we can begin to understand the importance of animals in their spiritual and practical lives, the development of early social structures, and the rudimentary beginnings of what would become a complex system of symbolic expression.
Preserving these ancient artworks is crucial, not only for the study of prehistoric cultures but also for the appreciation of the human journey and our collective heritage.
References
Cave art | Definition, Characteristics, Images, & Facts
https://www.britannica.com/art/cave-art
Cave painting – Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cave_painting
Cave Art Movement Overview | TheArtStory
https://www.theartstory.org/movement/cave-art
A Journey to the Oldest Cave Paintings in the World | History | Smithsonian Magazine
Smithsonian Magazine: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/journey-oldest-cave-paintings-world-180957685/